Copy(DicomDataSet,DicomElement,DicomElement,DicomCopyCallback) Method
public void Copy(DicomDataSet dataSet,DicomElement destination,DicomElement source,DicomCopyCallback callback)
- (BOOL)copyElementsInDataSet:(LTDicomDataSet *)dataSet destinationElement:(nullable LTDicomElement *)dst sourceElement:(nullable LTDicomElement *)src callback:(LTDicomCopyCallback)callback error:(NSError **)error; public void copy(DicomDataSet dataSet, DicomElement destElement, DicomElement srcElement, DicomCopyCallback callback) public:void Copy(DicomDataSet^ dataSet,DicomElement^ destination,DicomElement^ source,DicomCopyCallback^ callback)
Parameters
dataSet
The Data Set to be copied (the source Data Set).
destination
A data element within the destination Data Set. A copy of the source Data Set will be inserted as the child of this data element.
source
A data element within the source Data Set. All children, grandchildren, etc., of this element will be added to the destination Data Set.
callback
which will be called for each DicomElement in the DicomDataSet. This parameter cannot be null
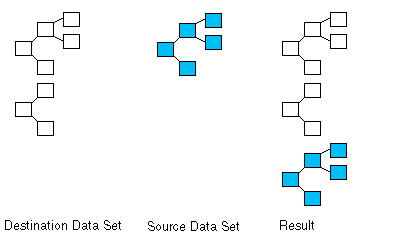
If both source and destination are null, the source Data Set will be inserted at the root level of the destination Data Set. Therefore the highest level elements of the source Data Set will be added as siblings to the highest level elements of the destination Data Set. This can be seen in the diagram below.
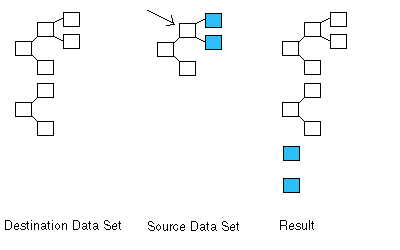
If source is not null and destination is null, the children of source will be added at the root level of the destination Data Set (i.e., as siblings to elements at the highest level). This can be seen in the diagram below. Note that the source elements to be added are in blue.
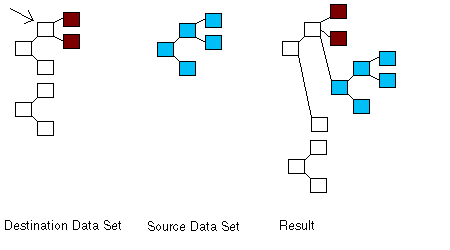
If source is null and destination is not null, the entire source Data Set will be added as children to destination. This can be seen in the diagram below.
If source and destination are both not null, then the children of source are added as the children of destination. This can be seen in the diagram below. The original children of destination are in red and the source elements to be added are in blue.
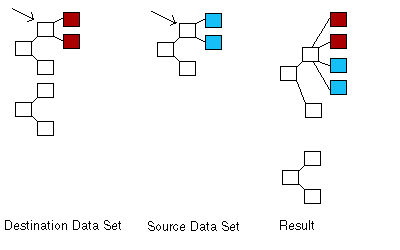
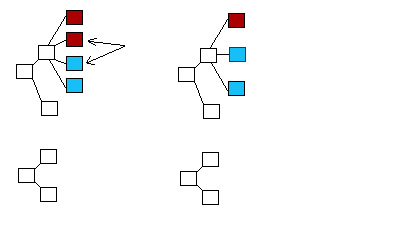
If an inserted element has the same tag value as a destination element at the same level and with the same parent, then the value from the source element is copied into the destination element and any child elements are added accordingly. For example, the diagram below shows the result of a call to Copy. If the two elements indicated by the arrows have the same tag value, the value from the source element is copied into the destination element and the structure on the right results. This is shown by the red outline of the destination element with the blue center of the source element.
To make the destination Data Set an exact copy of the source Data Set, instead of inserting it within the destination Data Set, you must call Reset on the destination Data Set, before calling Copy.
This overload of Copy will call callback to for each DicomElement in the DicomDataSet. The purpose of callback is to determine if a particular DicomElement is to be part of the copy. callback should return true to include the DicomElement in the copy. callback should return false to exclude the DicomElement in the copy.
This example copies a DICOM Dataset using a callback The callback allows you to select with DICOM elements to copy The example copies all elements except the pixel data element, and save the resulting dataset
using Leadtools;using Leadtools.Dicom;///private bool DicomCopyCallback(DicomElement element, DicomCopyFlags flags){if (element.Tag == DicomTag.PixelData)return false;return true;}private void DicomDataSet_CopyExample(DicomDataSet dsOriginal){DicomDataSet dsNew = new DicomDataSet();dsNew.Copy(dsOriginal, null, null, DicomCopyCallback);string sFile = Path.Combine(LEAD_VARS.ImagesDir, "test.dcm");dsNew.Save(sFile, DicomDataSetSaveFlags.None);string sMsg = string.Format("File Saved: {0}", sFile);Console.WriteLine(sMsg);}static class LEAD_VARS{public const string ImagesDir = @"C:\LEADTOOLS23\Resources\Images";}
© 1991-2025 Apryse Sofware Corp. All Rights Reserved.
