Queue - NodeJS
This tutorial shows how to queue tasks using the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services in a NodeJS application.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Summary | This tutorial covers how to make Queue requests and process the results using the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services in a NodeJS application. |
| Completion Time | 30 minutes |
| Project | Download tutorial project (125 KB) |
| Platform | LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API |
| IDE | Visual Studio 2019 |
| Language | NodeJS |
| Development License | Download LEADTOOLS |
| Try it in another language |
|
Required Knowledge
Be sure to review the following sites for information about LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API.
- Introduction and Service Call Requirements
- Required Parameters and Return Objects
- Cloud Services NodeJS Get Started with Tutorials
Application ID and Password
Create an Account with LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services to obtain both Application ID and Password strings.
Service Plans
LEADTOOLS Service Plan offerings:
| Service Plan | Description |
|---|---|
| Free Trial | Free Evaluation |
| Page Packages | Prepaid Page Packs |
| Subscriptions | Prepaid Monthly Processed Pages |
To further explore the offerings, refer to the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services page.
To obtain the necessary Application ID and Application Password, refer to Create an Account and Application with the LEADTOOLS Hosted Cloud Services.
Add the Queue Code
With the project created and the package added, coding can begin.
In the Solution Explorer, open server.js. Add the following variables at the top.
//Simple script to showcasing how to queue up and run multiple requests using the LEADTOOLS CloudServices.const axios = require("axios");//If uploading a file as multi-part content, we will need the file-system library installed.//const fs = require('fs');const servicesUrl = "https://azure.leadtools.com/api/";//The first page in the file to mark for processingconst firstPage = 1;//Sending a value of -1 will indicate to the services that the rest of the pages in the file should be processed.const lastPage = -1;//Enum corresponding to the output format for the file. For the purposes of this script, we will be converting to tif.const fileFormat = 4;//We will be uploading the file via a URl. Files can also be passed by adding a PostFile to the request. Only 1 file will be accepted per request.//The services will use the following priority when determining what a request is trying to do GUID > URL > Request Body Contentconst fileURL = "http://demo.leadtools.com/images/cloud_samples/ocr1-4.tif";let guid = "";const uploadUrl = servicesUrl + "UploadFile?fileurl=" + fileURL;
Add an axios.post call to process the uploadFile request as well as the uploadCallback function to capture the GUID and provide it to the next section.
This sends an uploadFile request to the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API, if successful, the file will be uploaded to the server and a unique identifier (GUID) will be returned and stored for later use.
axios.post(uploadUrl, {}, getRequestOptions(uploadUrl)).then((res) => {uploadCallback(res.error, res, res.data);}).catch((err) => {console.error(err);});//If uploading a file as multi-part content:/*const uploadUrl = servicesUrl + "UploadFile";const form = new FormData();form.append("file", fs.createReadStream('path\to\inputFile'));axios.post(uploadUrl, form, getRequestOptions(uploadUrl)).then((res) => {uploadCallback(res.error, res, res.data);}).catch ((err) => {console.error(err);});*/function uploadCallback(error, response, body) {if (!error && response.status === 200) {guid = body;console.log("Unique ID returned by the Services: " + guid);checkVerification();}}
After the file upload a verification check will be performed to ensure the files were submitted to the server. This function will also add a ExtractText request to the queue.
Create an async function called checkVerification() which utilizes the GUID from the uploadFile request.
async function checkVerification() {const queryUrl = servicesUrl + "Query?id=" + guid;await axios.post(queryUrl, {}, getRequestOptions(queryUrl)).then((res) => {const results = res.data;if (!res.error && results["FileStatus"] !== 123) {console.log("Verification finished with return code: " + res.status);if (results["FileStatus"] == 122) {const recognitionUrl =servicesUrl +"Recognition/ExtractText?firstPage=" +firstPage +"&lastPage=" +lastPage +"&guid=" +guid;axios.post(recognitionUrl, {}, getRequestOptions(recognitionUrl)).then((res) => {recognitionCallback(res.error, res, res.data);}).catch((err) => {console.error(err);});} else {console.log("File failed verification with File Status: " +results["FileStatus"]);}} else {//The file has not yet finished processing.return new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {//Sleep for 5 seconds before trying againresolve(checkVerification()); //Call the method again.}, 5000);});}}).catch((err) => {console.error(err);});}
Next create the callback functions recognitionCallback(error, response, body), conversionCallback(error, response, body), and runCallback(error, response, body).
The recognitionCallback function confirms the ExtractText request was queued and submits a Convert request using the same saved GUID information.
The conversionCallback function confirms the Convert request was queued and submits a Run request using the same saved GUID information to process the queue.
The runCallback function confirms the Run request was processed.
function recognitionCallback(error, response, body) {if (!error && response.status === 200) {console.log("ExtractText successfully queued");const conversionUrl =servicesUrl +"Conversion/Convert?firstPage=" +firstPage +"&lastPage=" +lastPage +"&guid=" +guid +"&format=" +fileFormat;axios.post(conversionUrl, {}, getRequestOptions(conversionUrl)).then((res) => {conversionCallback(res.error, res, res.data);}).catch((err) => {console.error(err);});} else {console.log("ExtractText failed to queue with HTTP code: " + response.status);console.log(body);}}function conversionCallback(error, response, body) {if (!error && response.status === 200) {console.log("Conversion successfully queued");const runUrl = servicesUrl + "Run?id=" + guid;axios.post(runUrl, {}, getRequestOptions(runUrl)).then((res) => {runCallback(res.error, res, res.data);}).catch((err) => {console.error(err);});} else {console.log("Conversion failed to queue with HTTP code: " + response.status);console.log(body);}}function runCallback(error, response, body) {if (!error && response.status === 200) {console.log("File has been successfully marked to run");queryServices();} else {console.log("Run failed with HTTP code: " + response.status);console.log(body);}}
Next, create an async function called queryServices(guid) that utilizes the GUID provided by Queue request.
If successful the response body will contain all the request data in JSON format.
async function queryServices() {//Function to query the status of a request. If the request has not yet finished, this function will recursively call itself until the file has finished.const queryUrl = servicesUrl + "Query?id=" + guid;await axios.post(queryUrl, {}, getRequestOptions(queryUrl)).then((res) => {const results = res.data;if (!res.error && results["FileStatus"] !== 100) {console.log("File finished processing with return code: " + res.status);if (results["FileStatus"] !== 200) {return;}console.log("Results: \n");parseJson(results["RequestData"]);} else {//The file has not yet finished processing.return new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {//Sleep for 5 seconds before trying againresolve(queryServices()); //Call the method again.}, 5000);});}}).catch((err) => {console.error(err);});}
Then, create the function parseJson(jsonObject) to process the returned JSON data.
function parseJson(jsonObject) {//Function to decode the JSON object that was returned by the LEADTOOLS CloudServices.for (let i = 0; i < jsonObject.length; i++) {let currentRequest = jsonObject[i];console.log("Service Type: " + currentRequest["ServiceType"]);if (currentRequest["ServiceType"] === "Recognition" &¤tRequest["RecognitionType"] === "Text") {console.log("Recognition Method: " + currentRequest["RecognitionType"]);console.log("Data:" + currentRequest["data"]);} else if (currentRequest["ServiceType"] === "Conversion") {console.log("Urls: ");currentRequest["urls"].forEach((url) => {console.log(url);});} else {console.log("Unanticipated service type");}}}
Finally, create the function getRequestOptions(url) to provide header and authorization to the axios.post connections in order to request the GUID and JSON data through.
Where it states Replace with Application ID and Replace with Application Password be sure to place your Application ID and Password accordingly.
function getRequestOptions(url) {const appId = "Replace with Application ID";const password = "Replace with Application Password";const token = Buffer.from(`${appId}:${password}`, "utf8").toString("base64");//Function to generate and return HTTP request options.const requestOptions = {url: url,data: {},//If uploading a file as multi-part content, remove the Content-Length header.headers: {"Content-Length": 0,Authorization: `Basic ${token}`,},};return requestOptions;}
Run the Project
Run the project by pressing Ctrl + F5, or by selecting Debug -> Start Without Debugging.
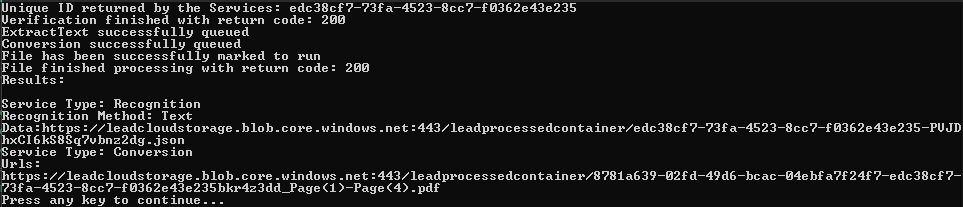
If the steps were followed correctly, the console appears and the application displays the parsed check information from the returned JSON data.
Wrap-up
This tutorial showed how to queue tasks via the LEADTOOLS Cloud Services API.
