|
Available in LEADTOOLS Medical Imaging toolkits. |
LDicomDS::DeleteElement
#include "Ltdic.h"
pDICOMELEMENT LDicomDS::DeleteElement(pElement)
|
pDICOMELEMENT pElement; |
/* pointer to a DICOMELEMENT structure */ |
Deletes the specified item from the Data Set.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
pElement |
Pointer to a DICOMELEMENT structure that contains the item to be deleted. |
Returns
|
!NULL |
A pointer to an adjacent item. If the item being deleted has a sibling (same level, same parent), following it, the returned pointer will point to this sibling. If the item being deleted does not have a sibling following it, but has a sibling preceding it, the returned pointer points to the preceding sibling. If the item being deleted is an only child, the returned pointer points to the parent. |
|
NULL |
The item being deleted has no siblings and no parent. |
Comments
You can remove all items from the Data Set using LDicomDS::ResetDS.
Since the Data Set is stored internally as a tree, the deletion must be carried out as a tree.
When deleting an item from the tree, if the item being deleted has a sibling (same level, same parent), following it, this function returns a pointer to this sibling. If the item being deleted does not have a sibling following it, but has a sibling preceding it, this function returns a pointer to the preceding sibling. If the item being deleted is an only child, this function returns a pointer to the parent. If there is no parent this function returns NULL.
Below are illustrations of these situations:
For the sake of these illustrations, the order of siblings is top to bottom. A preceding sibling is drawn above the sibling it precedes, a following sibling is drawn below the sibling it follows.
Please note that the numbering of the items of interest is arbitrary, and does not imply order.
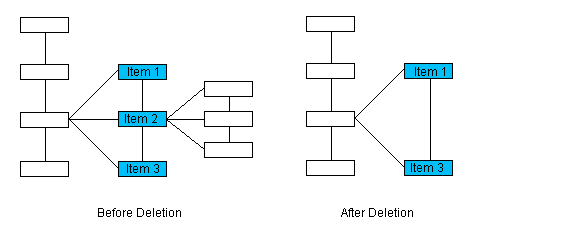
In this illustration item 2 will be deleted. Since it has a following sibling, the returned pointer will point to item 3.

In this illustration item 3 will be deleted. Since it does not have a following sibling, but does have a preceding sibling, the returned pointer will point to item 2.
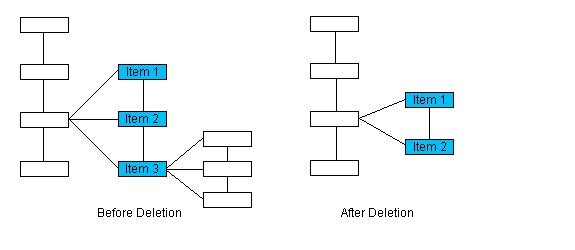
In this illustration item 2 will be deleted. Since it is an only child, the returned pointer will point to the parent, item 1.
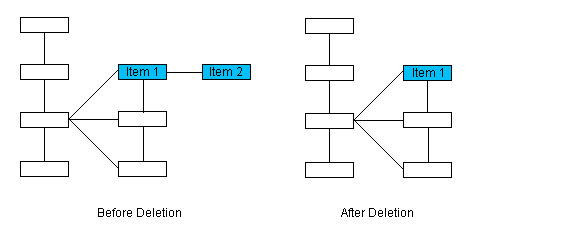
In this illustration item 1 will be deleted. Since it has no siblings and no parent, this function will return NULL.

Required DLLs and Libraries
|
LTDIC For a listing of the exact DLLs and Libraries needed, based on the toolkit version, refer to Files To Be Included With Your Application |
See Also
Example
This example removes an element from the Data Set.
L_INT LDicomDS_DeleteElementExample()
{
LDicomDS* pDS;
pDICOMELEMENT pElement;
pDS = new LDicomDS(NULL);
pDS->InitDS( CLASS_CT_IMAGE_STORAGE, 0);
pElement = pDS->FindFirstElement(NULL, TAG_PATIENT_NAME, FALSE);
if (pElement != NULL)
{
pDS->DeleteElement(pElement);
}
delete pDS;
return DICOM_SUCCESS;
}