LEAD AAC Encoder User Interface
The LEAD AAC Encoder implements Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), a high quality compression standard used with MPEG4 or H264 ISO MP4 files and iPod and PSP devices.
Key Features
-
Supports both variable and constant bitrates
-
Supports selection of output channels
-
Supports surround sound
-
Supports both versions of AAC: MPEG4 and MPEG2
-
Supports different profiles: Low Complexity, Main and Long Term Prediction
-
Supports 2 stream formats: Raw and ADTS
-
Supports selection of output sample frequency
-
Includes cutoff frequency option
-
Includes a force stereo output option in the decoder
Options for the LEAD AAC Encoder can be set manually through the encoder property page, which is shown in the figure below:
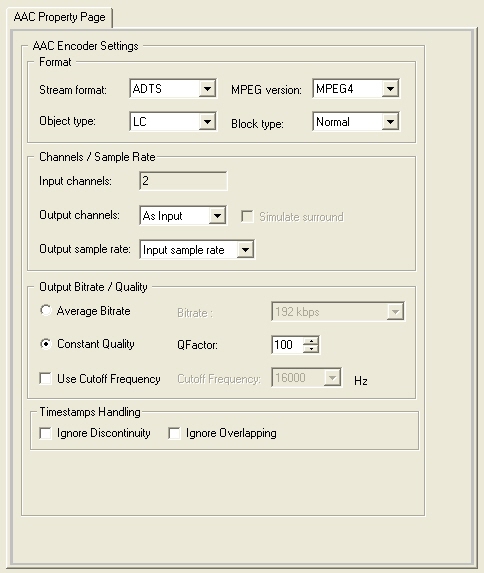
Changes will be applied only when the filter's state is stopped with the ability to set them permanently by selecting Apply or OK, or to abandon changes by selecting Cancel. Positioning the mouse pointer over a control displays general information for that control.
The following table shows the controls and their descriptions:
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Format | |
| Stream format drop-down list box | The format of the output stream. Selecting Raw will cause the MPEG Version drop-down list box contents to be restricted to MPEG4 only. |
| MPEG version drop-down list box | The AAC audio MPEG version. If MPEG2 is selected, only LC and MAIN object types will be listed in the Object type drop-down list box. |
| Object type drop-down list box | The AAC profile used. LC stands for Low Complexity; this option requires lower CPU and Memory resources. The MAIN profile offers more efficiency on the expense of more resources.The Long Term Prediction profile, LTP, is suitable for speech and signals with clear pitch property. The LTP option can be used with MPEG4 AAC only; MPEG4 must be selected in the MPEG4 Version drop-down list box. |
| Block type drop-down list box | The allowed block type; data window length. The long block is usually 1024 samples, while the short block is usually 128 samples. Normal means both blocks are allowed. |
| Channels / Sample Rate | |
| Input channels text box | The number of input audio channels. If the input pin is not connected, the box will contain the text Unknown. |
| Output channels drop-down list box | The number of output channels. You can select between, mono, stereo, 6 channels, or you can leave the output channels the same as the input channels. If 6 channels is selected, the Simulate surround check box will be enabled. |
| Simulate surround check box | Enables\disables surround feature simulation. It will simulate surround sound on 5.1 systems from a stereo or mono source.This check box will be enabled only if the Output channels drop-down list box has 6 channels selected. |
| Output sample rate drop-down list box | The desired output sample rate (samples per second). |
| Output Bitrate / Quality | |
| Average Bitrate (radio button and drop-down list box) | You can select between Average BitRate and Constant Quality. If the Average BitRate radio button is selected, the Bitrate drop-down list box next to it will be enabled and you can select one of the predefined bitrates. |
| Constant Quality (radio button and spin) | You can select between Average BitRate and Constant Quality. If the Constant Quality radio button is selected, the QFactor spin next to it will be enabled and you can select the desired quality factor. |
| Cutoff frequency (check box and drop-down list box) | The Use Cutoff Frequency check box enables or disables the usage of cutoff frequency. If the box is selected, the Cutoff Frequency combo box next to it will be enabled and you can select one of the predefined frequencies. |
| Timestamps Handling | |
| Ignore Discontinuity check box | If selected, causes the encoder to ignore discontinuities in the timestamps (time gaps) of the incoming audio samples. Sometimes this is needed to work around audio source timing problems. |
| Ignore Overlapping check box | If selected, causes the encoder to ignore overlapping in the timestamps of the incoming audio samples. Sometimes this is needed to work around audio source timing problems. |
