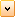
The Leadtools.Medical.Workstation.Client assembly is a component of the LEADTOOLS Medical Workstation Viewer. It uses the data access objects to Query the local database, retrieve DICOM instances from the local database, and store DICOM instances to the local database. This component uses the high-level PACS framework to Query/Retrieve from remote servers, and store images to remote servers.
The PACS Framework is a framework for easily creating DICOM-based servers. The framework consists of a Windows Service (Leadtools.Dicom.Service.exe) that implements a user-defined DICOM service. The Windows Service provides the following features:
- Handles DICOM connections
- Handles DICOM association negotiation
- Supports DICOM Message AddIns that allow user-supplied AddIns to respond to DICOM messages.
This framework allows the developer to quickly develop scalable full featured PACS (i.e. Windows Service, Association and secure communications, debug and audit log). It also allows the developer to organize DICOM services into different processes (i.e. LAN vs. WAN, secure vs. unsecure, HIS/RIS vs. PACS Archive).
The PACS Framework exposes specific interfaces that allow AddIns to implement additional functionality for the server. With AddIns you can:
- Specify supported presentation contexts
- Respond to specific DICOM messages
- Spy on DICOM communication without affecting the message
- Handle multiple DICOM messages with one AddIn.
The LEADTOOLS Medical Workstation Viewer is an end-user like application with functionality comparable to many DICOM viewers used today in the health care industry. It can be used without modification by medical professionals, by device manufacturers (as a Modality Workstation viewer), research facilities, or anyone that has a need for viewing DICOM images. The source code is provided for easy customization and branding. The workstation is built on LEADTOOLS PACS Framework components, and supports:
- DICOM SCU Query/Retrieve, Store, Storage Commit
- DICOM SCP service to provide Query/Retrieve and Store
- DICOM Media import
- Medical Image Viewing (display layouts, annotations, Zoom, Pan, Window-Level tools, etc)
- User Access Control (part of the demo)
For more information, refer to: