| Visual Basic (Declaration) | |
|---|---|
Public Class LocalHistogramEqualizeCommand Inherits RasterCommand Implements IRasterCommand | |
| Visual Basic (Usage) |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
| |
| C# | |
|---|---|
public class LocalHistogramEqualizeCommand : RasterCommand, IRasterCommand | |
| C++/CLI | |
|---|---|
public ref class LocalHistogramEqualizeCommand : public RasterCommand, IRasterCommand | |
Run the LocalHistogramEqualizeCommand on an image.
| Visual Basic |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
Public Sub LocalHistogramEqualizeCommandExample() | |
| C# |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
public void LocalHistogramEqualizeCommandExample() | |
This class applies the histogram equalizer locally on the image. The image is divided into local rectangles of dimension (Width, Height). The number of pixels inside each local rectangle are linearized according the histogram calculated for an extended rectangle around each local rectangle. The extended rectangles are of dimension:
((Width+2 * WidthExtension) , ( Height + 2 * HeightExtension)).
For an example, see the following drawing: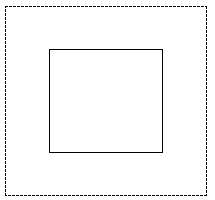
A rectangle and its associated extension, where the histogram is calculated.Use this class to bring out details in an image that has portions that are too dark or too bright. An example of this is a picture taken with a flashlight in a dark room. In such a picture, the subject receives good light while the background is very dark. The application of the local histogram brings out details, but creates a blocky artifact. Use Smooth to reduce the blockiness of the result. This class supports 12 and 16-bit grayscale and 48 and 64-bit color images. Support for 12 and 16-bit grayscale and 48 and 64-bit color images is available only in the Document/Medical toolkits. This command does not support 32-bit grayscale images.
System.Object
Leadtools.ImageProcessing.RasterCommand
Leadtools.ImageProcessing.Color.LocalHistogramEqualizeCommand
Target Platforms: Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, Windows Millennium Edition, Windows 2000, Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, Windows Server 2003 family
Reference
LocalHistogramEqualizeCommand MembersLeadtools.ImageProcessing.Color Namespace
Changing Brightness and Contrast
ChangeIntensityCommand Class
GammaCorrectCommand Class
ChangeContrastCommand Class
HistogramContrastCommand Class
StretchIntensityCommand Class
RemapIntensityCommand Class
InvertCommand Class
ChangeHueCommand Class
ChangeSaturationCommand Class
FillCommand
HistogramCommand Class
WindowLevelCommand
AutoColorLevelCommand Class
ColorLevelCommand Class
CorrelationListCommand
GrayScaleToDuotoneCommand Class
GrayScaleToMultitoneCommand Class
HolePunchRemoveCommand
SelectiveColorCommand Class
SkeletonCommand